A brain stroke, also known as a cerebrovascular accident (CVA) or stroke, occurs when there's a
disruption of blood flow to the brain. This disruption can lead to brain cell damage and various
neurological symptoms. Strokes are a medical emergency and require prompt attention to minimize
potential damage and improve outcomes.
Types of Brain Stroke
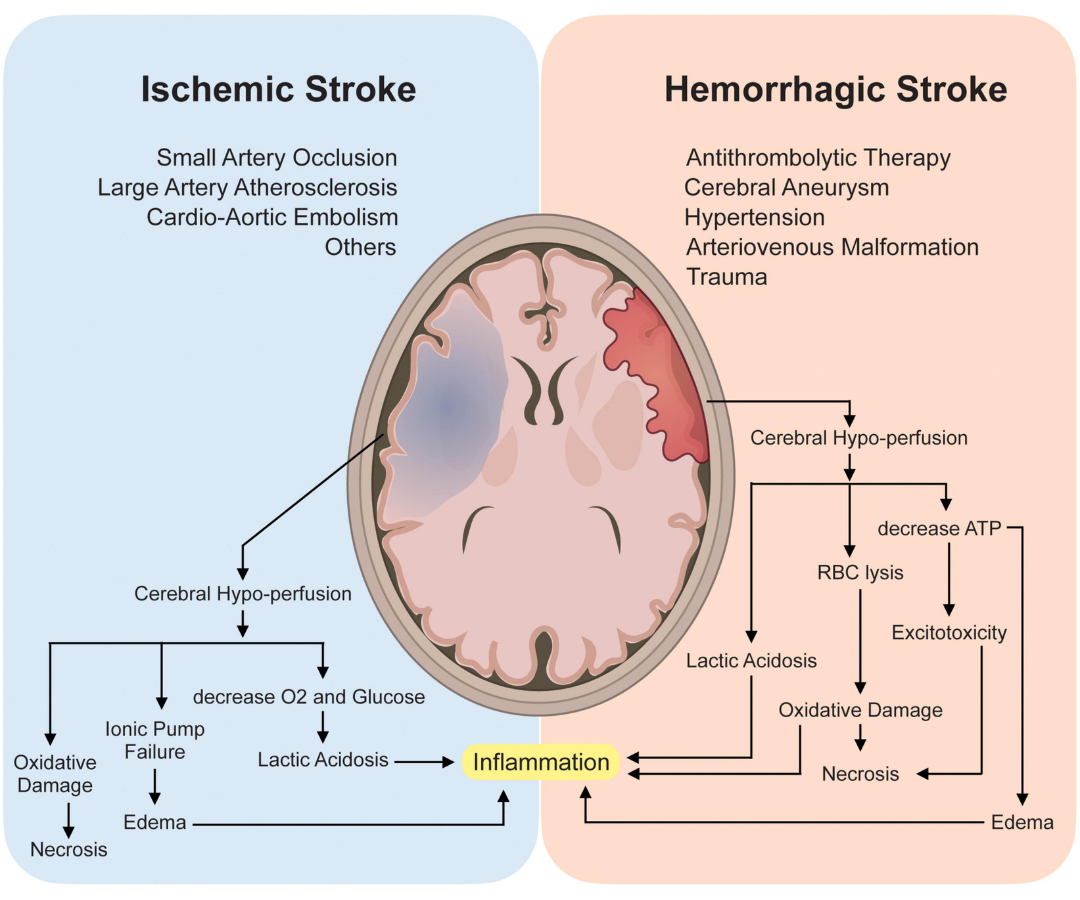
Ischemic Stroke: This type of stroke occurs when a blood clot or plaque buildup narrows or blocks an artery supplying blood to the brain. This can lead to a lack of oxygen and nutrients, causing brain tissue damage. Ischemic strokes account for the majority of stroke cases.
Hemorrhagic Stroke: A hemorrhagic stroke occurs when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures and causes bleeding within the brain tissue or in the spaces surrounding the brain. This bleeding can put pressure on brain tissue and cause damage.
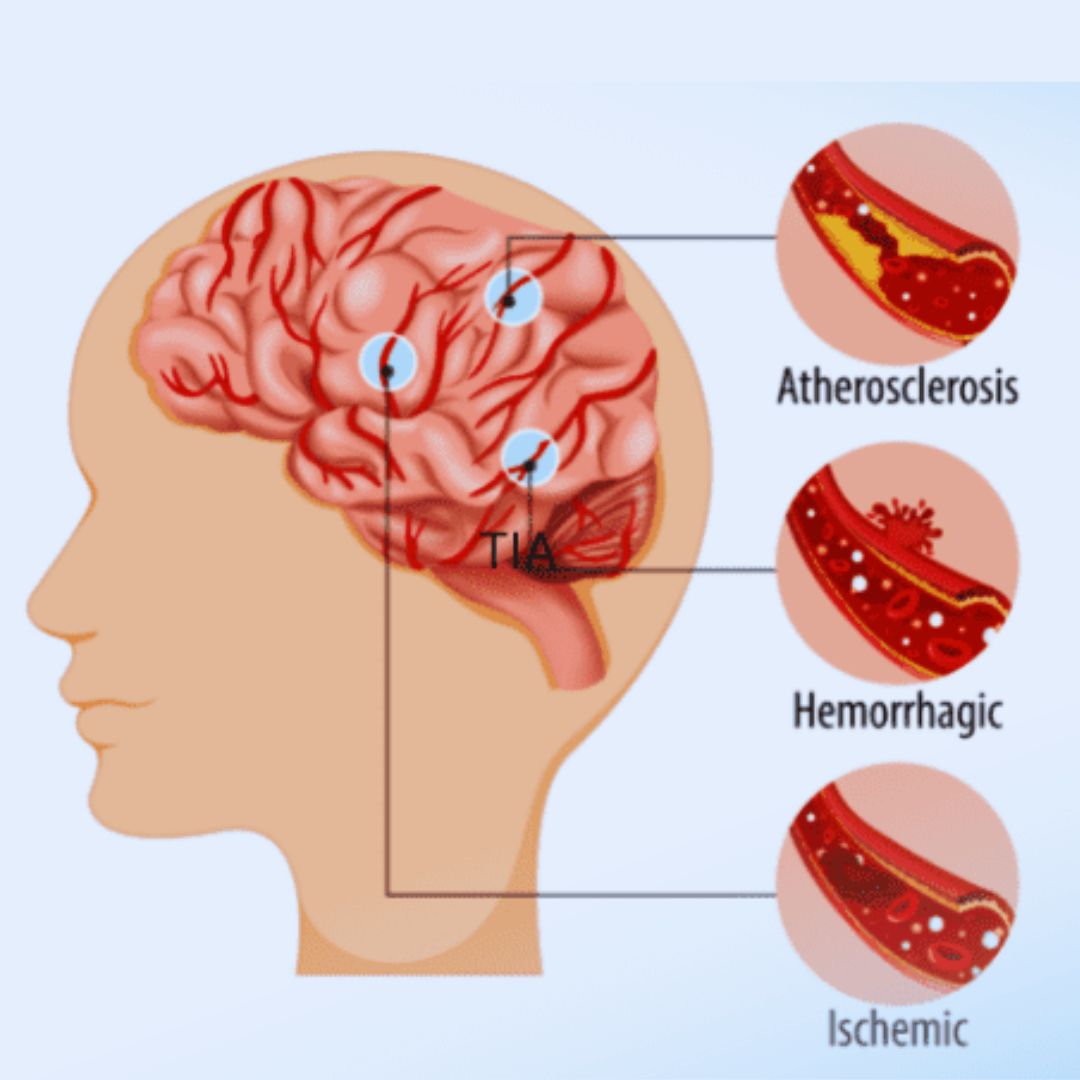
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Ischemic Stroke: Common causes include blood clots that form within the brain's blood vessels (thrombosis), blood clots that travel to the brain from other parts of the body (embolism), and narrowing of blood vessels due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup).
- Hemorrhagic Stroke: Causes include high blood pressure (hypertension), aneurysms (weakened blood vessel walls), arteriovenous malformations (abnormal blood vessel connections), and certain blood-thinning medications.
Recovery and Rehabilitation:
- Stroke survivors often require rehabilitation to regain lost functions and improve their quality of life. Rehabilitation can include physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and more.
- Recovery varies widely depending on factors such as the severity of the stroke and the effectiveness of treatment.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- A stroke is a medical emergency. If someone is suspected of having a stroke, they should seek immediate medical attention.
- Diagnosis involves medical history, physical examination, brain imaging (such as CT scan or MRI), and other tests to determine the type, location, and extent of the stroke.
- Treatment options depend on the type of stroke and may include clot-dissolving medication (thrombolytics) for ischemic strokes, and surgical intervention or medication to manage bleeding in hemorrhagic strokes.
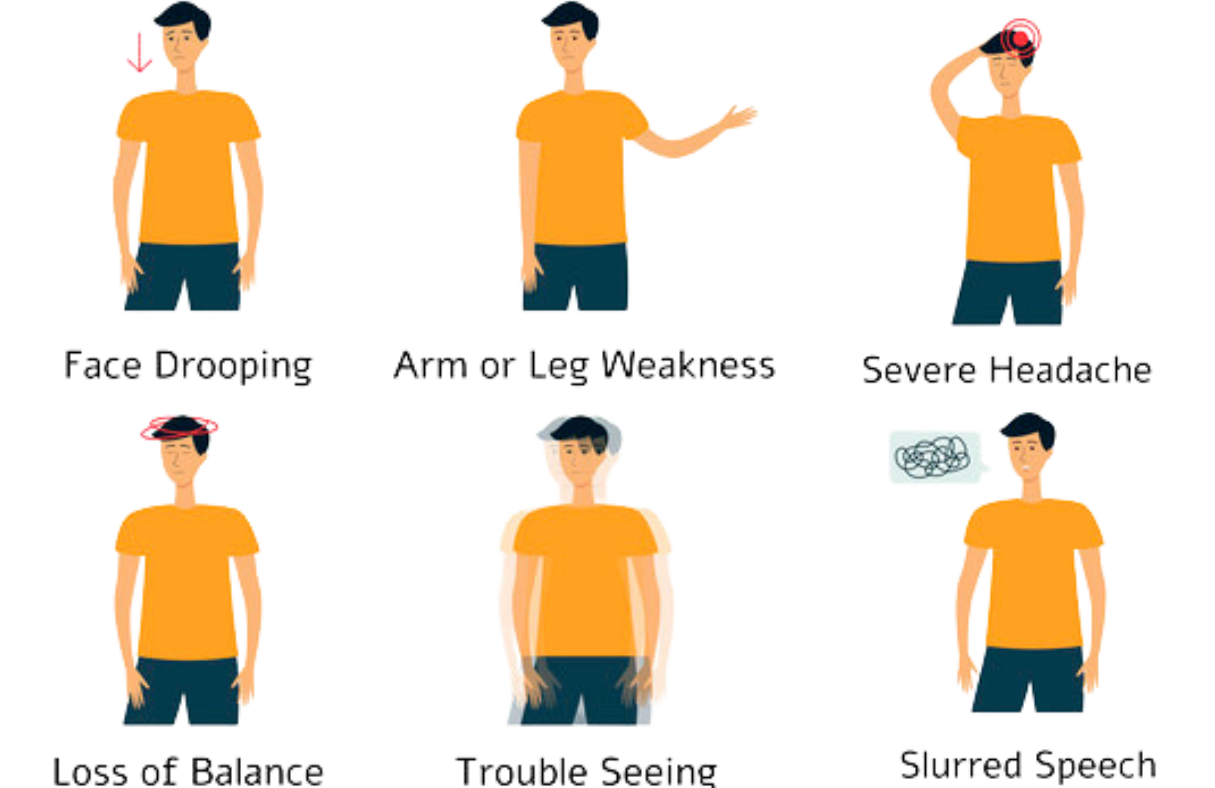
Symptoms:
- Sudden weakness or numbness, often on one side of the body.
- Sudden confusion, trouble speaking, or difficulty understanding speech.
- Sudden severe headache with no apparent cause.
- Sudden trouble walking, loss of balance, dizziness, or coordination problems.
- Sudden vision changes, such as blurred or blackened vision.
