
Multiple sclerosis (MS) is a chronic autoimmune disease that affects the central nervous system, including the brain, spinal cord, and optic nerves. MS occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks the protective covering of nerve fibers, called myelin, causing inflammation and damage. This damage disrupts the normal flow of nerve impulses and can lead to a wide range of neurological symptoms.
Key Characteristics:
- Relapsing-Remitting MS (RRMS): The most common form of MS, characterized by episodes of new or worsening symptoms (relapses) followed by periods of partial or complete recovery (remissions).
- Primary Progressive MS (PPMS): This form involves a steady worsening of symptoms without distinct relapses or remissions.
- Secondary Progressive MS (SPMS): Initially, individuals with RRMS may experience relapses and remissions. Over time, many people transition to a progressive phase with a gradual worsening of symptoms.
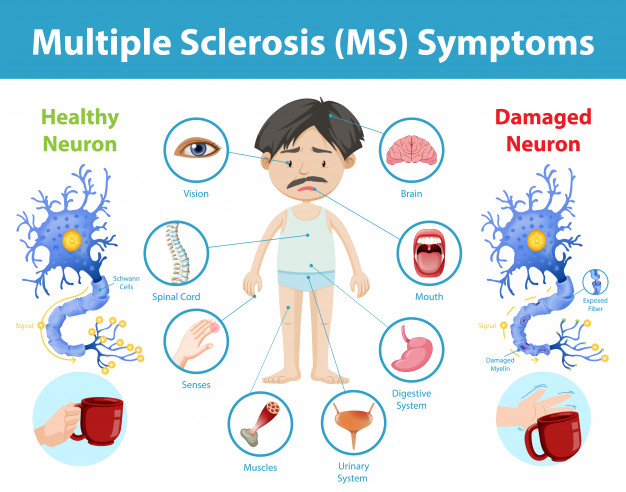
- Symptoms: MS symptoms vary widely and can affect mobility, sensation, coordination, vision, and cognitive function. Common symptoms include fatigue, difficulty walking, numbness or tingling, muscle weakness, vision problems, and issues with balance and coordination.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- The exact cause of MS is not fully understood. Genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
- MS is more common in certain populations and regions with higher latitudes.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, neurological examination, imaging (MRI), and tests to assess nerve function (evoked potentials).
- The diagnostic process may involve ruling out other conditions with similar symptoms.
Lifestyle and Emotional Well-being:
- MS can have significant emotional and psychological impacts. Support from healthcare professionals, support groups, and counseling can help manage these challenges.
- A positive outlook, social engagement, and maintaining hobbies and interests can contribute to overall well-being.

Treatment and Management:
- While there is no cure for MS, various treatments aim to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
- Disease-Modifying Therapies (DMTs): These medications can reduce the frequency and severity of relapses in relapsing forms of MS. They work by modifying the immune response.
- Symptomatic Treatment: Medications and therapies can address specific symptoms such as fatigue, muscle spasms, pain, and bladder or bowel issues.
- Physical and Occupational Therapy: Exercises, stretches, and mobility strategies can help manage muscle weakness and improve overall function.
- Cognitive Rehabilitation: Strategies to cope with cognitive challenges, such as memory problems and difficulty concentrating.
- Lifestyle Management: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle with regular exercise, a balanced diet, adequate sleep, stress management, and avoiding smoking is important for managing MS.
