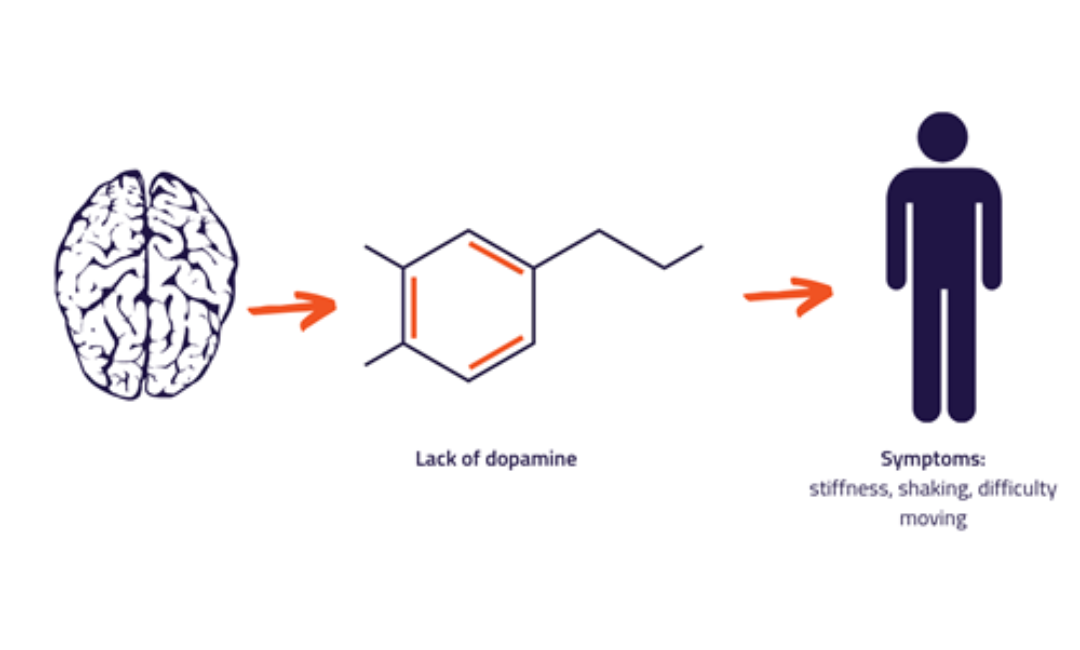
Parkinson's disease is a chronic and progressive neurological disorder that primarily affects movement and motor control. It develops due to the gradual degeneration of certain nerve cells in the brain that produce dopamine, a neurotransmitter responsible for facilitating smooth, coordinated movements. The loss of dopamine-producing cells leads to the characteristic symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
Key Characteristics:
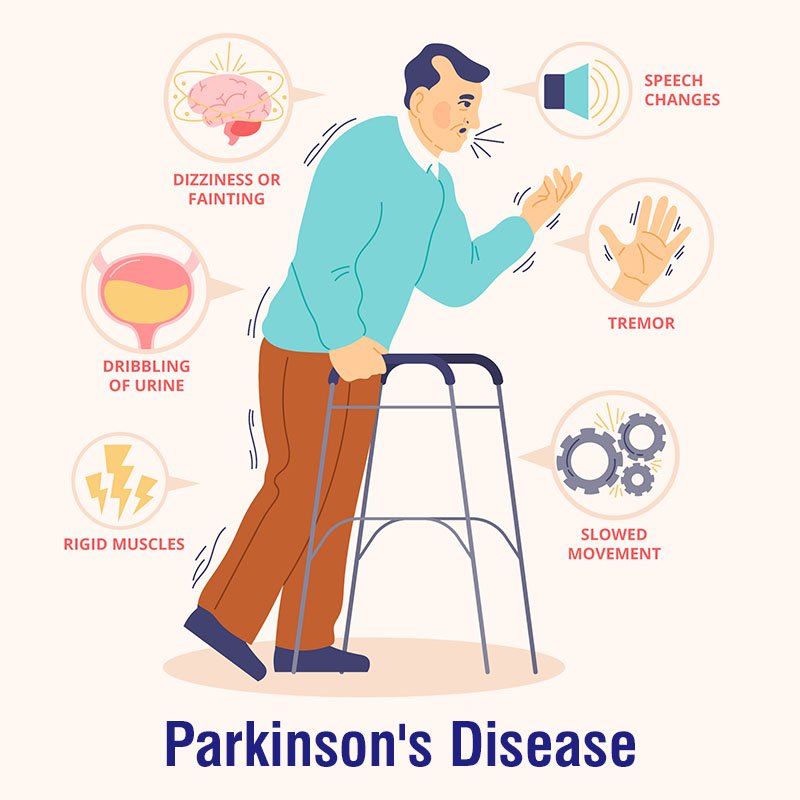
- Tremors: Resting tremors (shaking) are a hallmark symptom of Parkinson's. These tremors often start in the hands or fingers when they are at rest and decrease or disappear with purposeful movement.
- Bradykinesia: This refers to slowness of movement. People with Parkinson's may experience difficulty initiating and executing movements, making simple tasks take longer.
- Muscle Rigidity: Muscles become stiff and rigid, which can lead to discomfort and limit range of motion.
- Postural Instability: Individuals with Parkinson's often have difficulty maintaining balance and an upright posture, making them more prone to falls.
- Changes in Walking: Walking might involve shuffling steps, reduced arm swing, and a stooped posture.
- Speech and Swallowing Changes: Speech may become softer or more monotone, and swallowing difficulties (dysphagia) can occur.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- The exact cause of Parkinson's disease is not fully understood. Genetic and environmental factors are believed to play a role.
- Advanced age is the most significant risk factor, but early-onset cases can also occur.
Diagnosis and Stages:
- Diagnosis is primarily based on clinical evaluation, medical history, and observation of symptoms. There is no definitive test for Parkinson's disease.
- The disease progression is often categorized into stages, with the Hoehn and Yahr scale being commonly used. These stages help healthcare professionals assess the severity of symptoms and plan appropriate management.
Lifestyle Management:
- Staying physically active, maintaining a healthy diet, getting sufficient rest, and managing stress can contribute to overall well-being for individuals with Parkinson's.
- Support groups and psychological counseling can help manage emotional and psychological challenges associated with the disease.
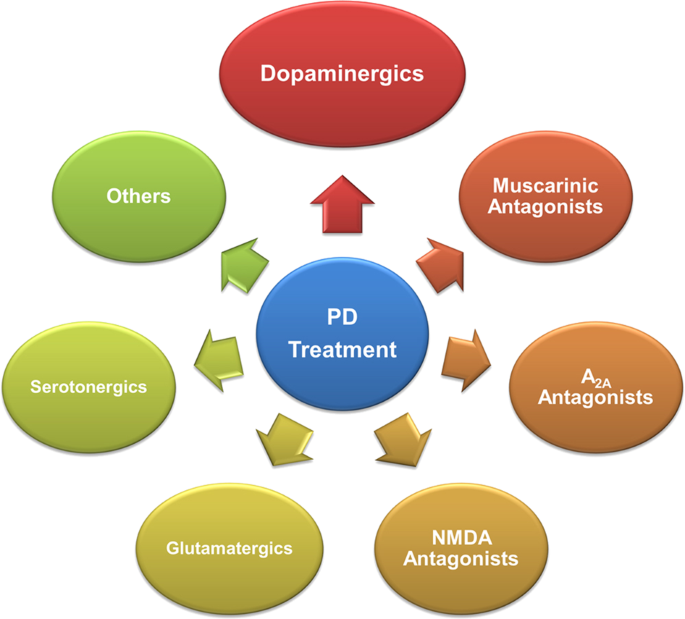
Treatment and Management:
- While there is no cure for Parkinson's, various treatments aim to manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
- Medications: Dopamine replacement therapies, such as levodopa, are commonly prescribed to alleviate motor symptoms. Other medications target specific symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
- Surgery: Deep brain stimulation (DBS) involves implanting electrodes in specific brain regions to help control motor symptoms. This is typically considered for individuals whose symptoms do not respond well to medications.
- Physical Therapy: Exercises and movement strategies can help improve mobility, balance, and overall physical function.
- Speech Therapy: Speech and swallowing exercises can address communication and swallowing difficulties.
- Occupational Therapy: Techniques to adapt to daily tasks and maintain independence are provided by occupational therapists.
