Migraine headaches are a type of recurring headache that can cause intense pain and other symptoms. They are often characterized by a throbbing or pulsating pain, usually on one side of the head, but they can also affect both sides. Migraines are more than just headaches; they can involve a complex interplay of neurological and vascular factors.
Types of Migraines:
Migraine without Aura: The most common type, characterized by moderate to severe headache pain without the presence of an aura.
Migraine with Aura: This type involves the presence of auras before or during the headache phase. Auras can affect vision, sensation, and speech.
Chronic Migraine: Migraines that occur on 15 or more days per month for at least three months, with at least eight of those being migraines.
Causes and Triggers:
- The exact cause of migraines is not fully understood, but genetics, changes in brain chemistry, and abnormalities in brain function are believed to play a role.
- Migraines can be triggered by various factors, including hormonal changes, certain foods (such as aged cheeses and processed meats), caffeine, alcohol, stress, changes in sleep patterns, and environmental factors.
Diagnosis and Treatment:
- Maintaining a regular sleep schedule, managing stress, staying hydrated, and avoiding trigger factors can help reduce the frequency and severity of migraines.
- Keeping a migraine diary to track triggers, symptoms, and patterns can be helpful in managing the condition.
Lifestyle Management:
- Diagnosis is typically based on a detailed medical history and a description of symptoms. There is no definitive test for migraines.
- Treatment aims to prevent migraine attacks or manage symptoms when they occur. It can involve lifestyle changes, medications, and identifying and avoiding triggers.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers, such as ibuprofen or aspirin, might help with mild migraines. For more severe migraines, prescription medications like triptans or preventive medications may be prescribed.
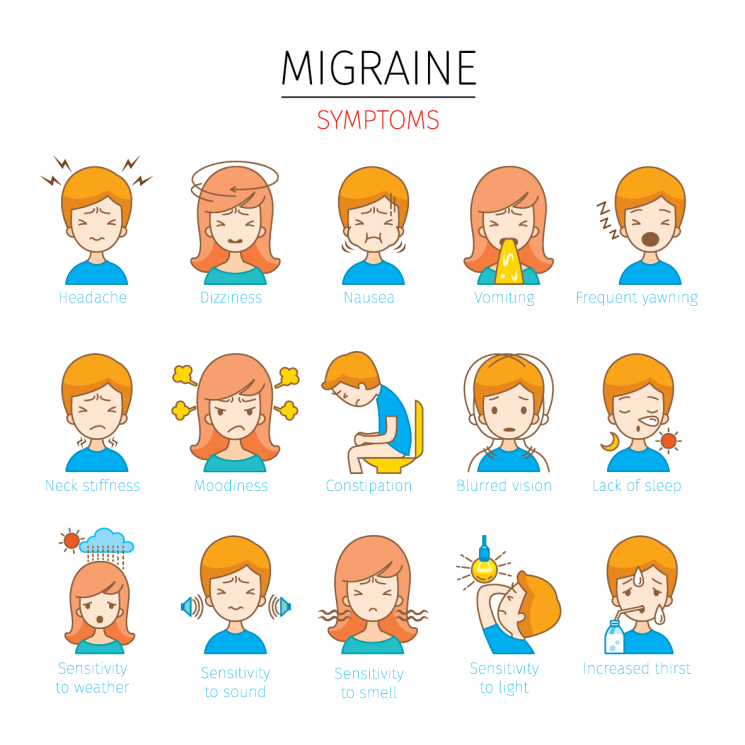
Symptoms:
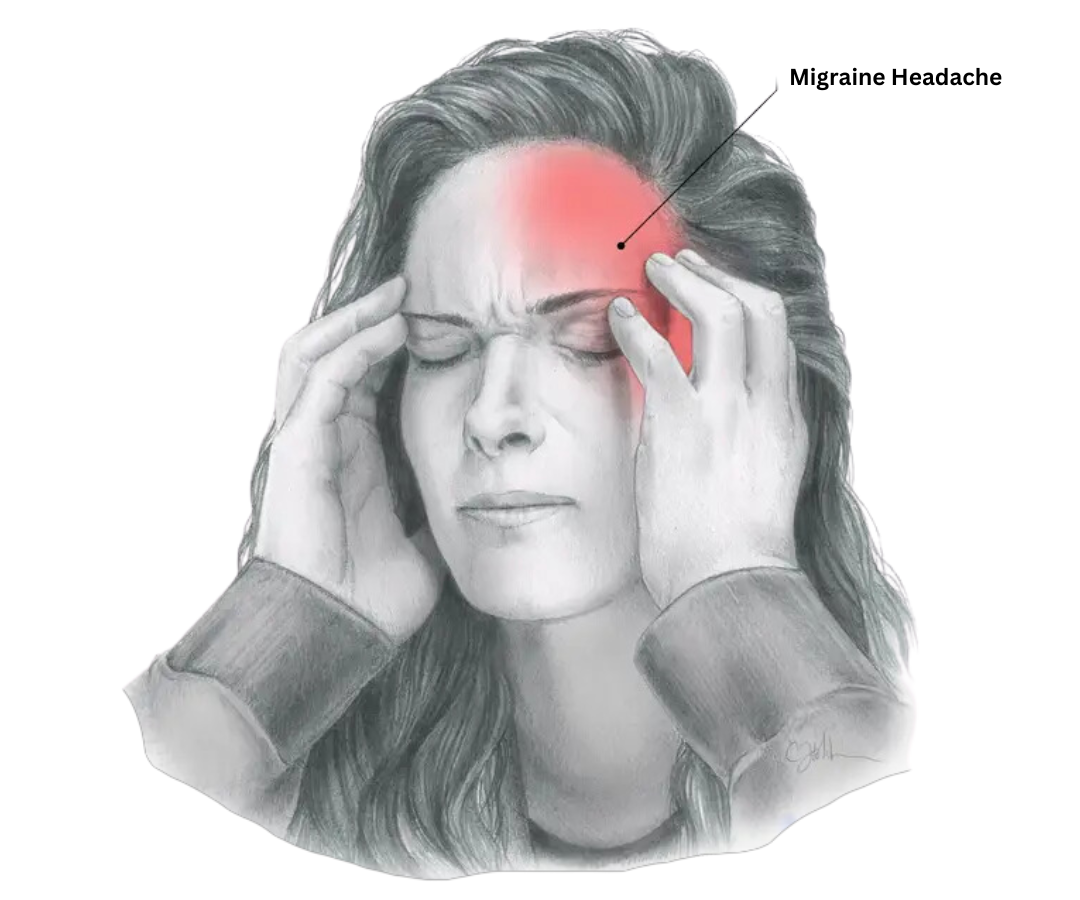
- Pain: The pain of a migraine is typically moderate to severe and often described as throbbing or pulsating. It can last for hours to days.
- Location: Migraine pain often affects one side of the head, but it can spread to both sides. The pain is commonly felt around the temples, forehead, and eyes.
- Auras: Some people experience auras before the onset of a migraine. Auras are visual disturbances such as flashing lights, zigzag lines, or temporary vision loss.
- Sensitivity to Light and Sound: Sensitivity to light (photophobia) and sound (phonophobia) is common during a migraine attack.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Many individuals with migraines experience nausea and vomiting during an attack.
- Other Symptoms: Migraines can also lead to fatigue, dizziness, difficulty concentrating, and irritability.