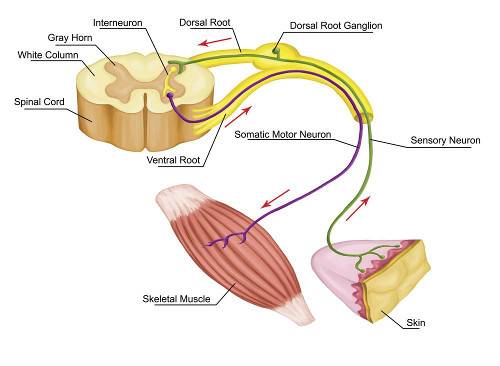
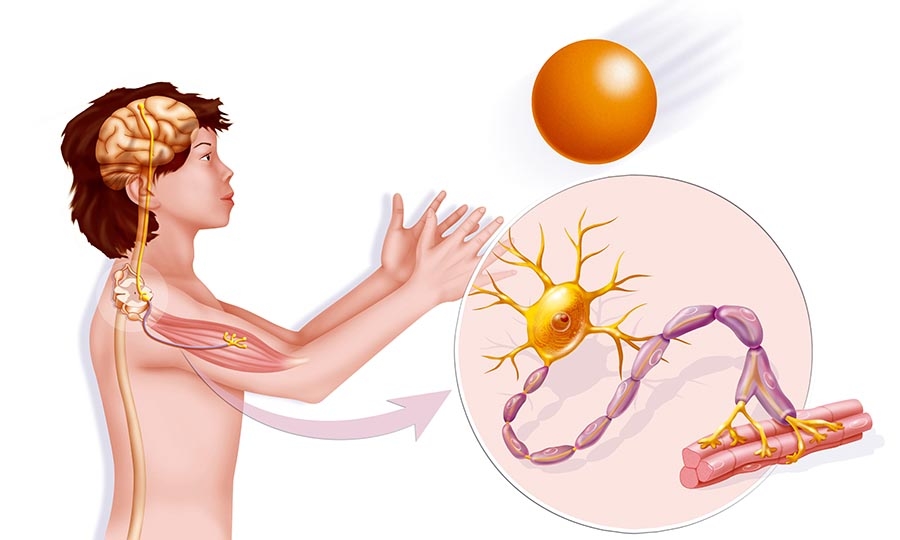
Neuromuscular diseases (NMDs) encompass a diverse group of disorders that affect the communication between the nervous system and muscles. These diseases can result in muscle weakness, impaired coordination, muscle wasting, and other motor and sensory symptoms. NMDs can originate from various causes, including genetic mutations, autoimmune reactions, infections, and metabolic abnormalities.
Key Characteristics:
- Muscle Weakness: One of the most common and prominent symptoms of NMDs is muscle weakness, which can affect mobility, dexterity, and overall physical function.
- Muscle Wasting: Some NMDs lead to the progressive loss of muscle mass, causing a decline in strength and function.
- Coordination Issues: Impaired coordination, balance problems, and difficulties with fine motor skills are common in some NMDs.
- Sensory Changes: Some NMDs can cause changes in sensation, such as numbness, tingling, or pain.
- Breathing and Swallowing Issues: Depending on the specific NMD, respiratory muscles and muscles involved in swallowing might be affected, leading to respiratory problems and difficulty eating.
Types of Neuromuscular Diseases:
- Muscular Dystrophies: Genetic disorders characterized by progressive muscle weakness and wasting due to the absence or dysfunction of specific proteins.
- Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis (ALS): Also known as Lou Gehrig's disease, ALS affects nerve cells in the brain and spinal cord, leading to muscle weakness and eventual paralysis.
- Myasthenia Gravis: An autoimmune disorder that impairs communication between nerves and muscles, causing muscle weakness and fatigue.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Nerve damage in the peripheral nervous system, leading to symptoms like numbness, tingling, and weakness.
- Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): A genetic disorder affecting the nerve cells in the spinal cord, resulting in muscle weakness and atrophy.
- Charcot-Marie-Tooth Disease:A group of inherited disorders affecting peripheral nerves, leading to muscle weakness and sensory changes.
- Guillain-Barré Syndrome: An autoimmune disorder causing sudden-onset muscle weakness and paralysis, often triggered by infections.
Causes and Risk Factors:
- Genetics: Many NMDs have a genetic basis, meaning they result from inherited gene mutations.
- Autoimmune Reactions:Some NMDs occur due to the immune system attacking nerve cells or muscle tissues.
- Infections: Certain infections can trigger NMDs, such as Guillain-Barré syndrome.
- Metabolic Abnormalities: Disorders affecting metabolic processes can lead to NMDs.
Diagnosis and Evaluation:
- Diagnosis involves a combination of medical history, physical examination, neurological assessments, and specialized tests like electromyography (EMG) and nerve conduction studies.
- Genetic testing may be used to identify specific gene mutations associated with certain NMDs.
Prognosis:
- The prognosis varies widely depending on the specific NMD, its severity, the individual's response to treatment, and the progression of the disease.
- Some NMDs are progressive and may lead to significant disability, while others might have less severe outcomes.
Treatment and Management:
- Treatment aims to manage symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
- Approaches include physical and occupational therapy, medication to manage symptoms and inflammation, assistive devices, and lifestyle modifications.
- For some genetic NMDs, specific treatments targeting the underlying genetic cause are being developed.
